Raycasting
Raycasting is an important technique in game development, used for detecting objects and interactions within a 3D environment. It allows you to "cast" an invisible line, or ray, through the scene to determine what it intersects with.
Raycasting is widely used in game development for:
- Object Interaction: Checking what the player is looking at or pointing to, such as selecting objects or NPCs.
- Shooting: Detecting hits when firing projectiles or bullets.
- Line-of-Sight Checks: Verifying if an enemy can see the player.
Commands
Leadwerks provides three commands for performing raycasting:
- World:Pick: Casts a ray between two specific points in the world space.
- Camera:Pick: Casts a ray from a screen coordinate into the 3D scene, useful for mouse picking or targeting.
- Entity:GetVisible: Casts a ray between two entities and returns true if nothing is hit.
The first two commands both return a PickInfo structure containing information about the intersection:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| entity | Entity | picked entity |
| face | Face | picked face, for brushes |
| mesh | Mesh | picked mesh, for models |
| meshlayer | integer | index of picked mesh layer |
| meshlayerinstance | iVec2 | picked mesh layer instance coordinate |
| normal | Vec3 | picked normal |
| polygon | integer | picked polygon, for models |
| position | Vec3 | picked position |
| texcoords | table | array of picked texture coordinates, for brushes or models |
Line-of-Sight Testing
This example demonstrates how a simple line-of-sight test can be performed to check if two entities can "see" each other.
-- Get the displays
local displays = GetDisplays()
-- Create window
local window = CreateWindow("Leadwerks", 0, 0, 1280 * displays[1].scale, 720 * displays[1].scale, displays[1], WINDOW_CENTER | WINDOW_TITLEBAR)
-- Create world
local world = CreateWorld()
-- Create framebuffer
local framebuffer = CreateFramebuffer(window)
-- Set up camera
local camera = CreateCamera(world)
camera:SetClearColor(0.125)
camera:SetPosition(0, 0, -6)
--Create two boxes
local box1 = CreateBox(world)
box1:SetPosition(-3,0,0)
local box2 = CreateBox(world)
box2:SetPosition(3,0,0)
--Create a wall between the two objects
local wall = CreateBox(world,1,2,1)
while not window:Closed() and not window:KeyDown(KEY_ESCAPE) do
--Move one box with the arrow keys
if window:KeyDown(KEY_UP) then box2:Move(0,0.1,0) end
if window:KeyDown(KEY_DOWN) then box2:Move(0,-0.1,0) end
--Perform the visibility test and show the results
if box2:GetVisible(box1) then
box1:SetColor(0,1,0)
box2:SetColor(0,1,0)
else
box1:SetColor(1,0,0)
box2:SetColor(1,0,0)
end
-- Update the world
world:Update()
-- Render the world
world:Render(framebuffer)
endUse the arrow keys to move one of the boxes up and down. You can see the boxes change color based on their visibility.

Raycast
This example shows how to use the World:Pick command:
-- Get the displays
local displays = GetDisplays()
-- Create window
local window = CreateWindow("Leadwerks", 0, 0, 1280 * displays[1].scale, 720 * displays[1].scale, displays[1], WINDOW_CENTER | WINDOW_TITLEBAR)
-- Create world
local world = CreateWorld()
-- Create framebuffer
local framebuffer = CreateFramebuffer(window)
-- Set up camera
local camera = CreateCamera(world)
camera:SetClearColor(0.125)
camera:SetFov(70)
camera:SetPosition(0, 2, -3)
camera:SetRotation(25, 0, 0)
-- Add a light
local light = CreateDirectionalLight(world)
light:SetRotation(35, 45, 0)
-- Set up the scene
local floor = CreatePlane(world, 100, 100)
floor:Move(0, -1, 0)
floor:SetColor(0.5)
local b1 = CreateBox(world, 2.0)
b1:SetPosition(-3.0, 0.0, 0.0)
b1:SetColor(1, 0, 0)
local b2 = CreateBox(world, 2.0)
b2:SetColor(0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
b2:SetPosition(3.0, 0.0, 2.0)
b2:SetRotation(0.0, 45.0, 0.0)
local pivot = CreatePivot(world)
local rod_scale = 5.0
local rod = CreateCylinder(world, 0.05)
rod:SetCollider(nil)
rod:SetParent(pivot)
rod:SetRotation(90.0, 0.0, 0.0)
rod:SetPosition(0.0, 0.0, rod_scale / 2.0)
rod:SetScale(1.0, rod_scale, 1.0)
local sphere = CreateSphere(world, 0.25)
sphere:SetCollider(nil)
sphere:SetParent(pivot)
sphere:SetColor(0, 1, 0)
sphere:SetPosition(0.0, 0.0, rod_scale)
while not window:Closed() and not window:KeyDown(KEY_ESCAPE) do
--Rotate the assembly
pivot:Turn(0.0, 0.5, 0.0)
--Get the point at the maximum ray distance
local target_pos = TransformPoint(0, 0, rod_scale, pivot, nil)
-- Perform a ray cast
local pickinfo = world:Pick(pivot:GetPosition(true), target_pos, 0.0, true)
--Update the sphere based on the pick result
if pickinfo.entity then
sphere:SetPosition(pickinfo.position, true)
else
sphere:SetPosition(target_pos, true)
end
-- Update the world
world:Update()
-- Render the world
world:Render(framebuffer)
endThe example shows a raycast with a vector that slowly rotates. A sphere is positioned at the raycast hit position to show where it intersects the scene.
Sphere Casting
Raycasts can include an optional radius parameter. When a non-zero radius is specified, the raycast becomes a sphere cast, which checks for intersections within a spherical volume. This is especially useful for detecting wider objects or simulating a more forgiving collision area.
If we add the sphere radius into the pick command, the picked position will now correctly show the point at which the sphere would hit the scene:
local pick_info = world:Pick(pivot:GetPosition(true), target_pos, 0.25, true)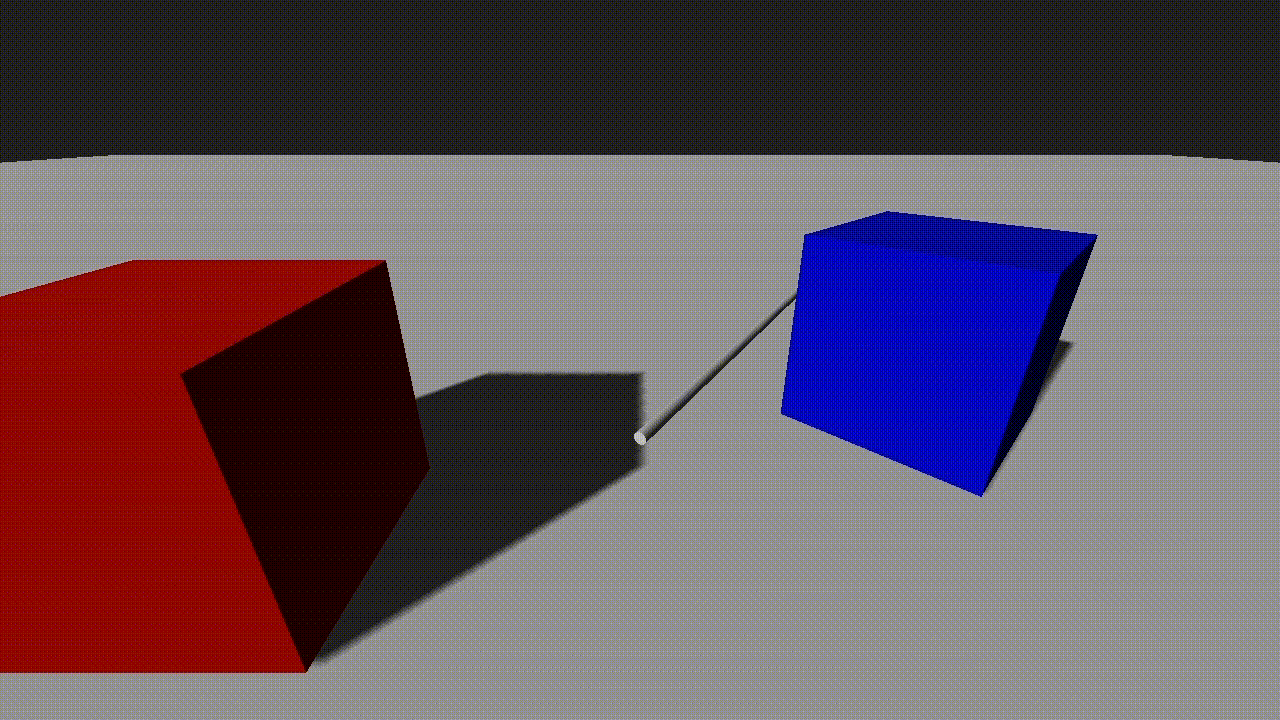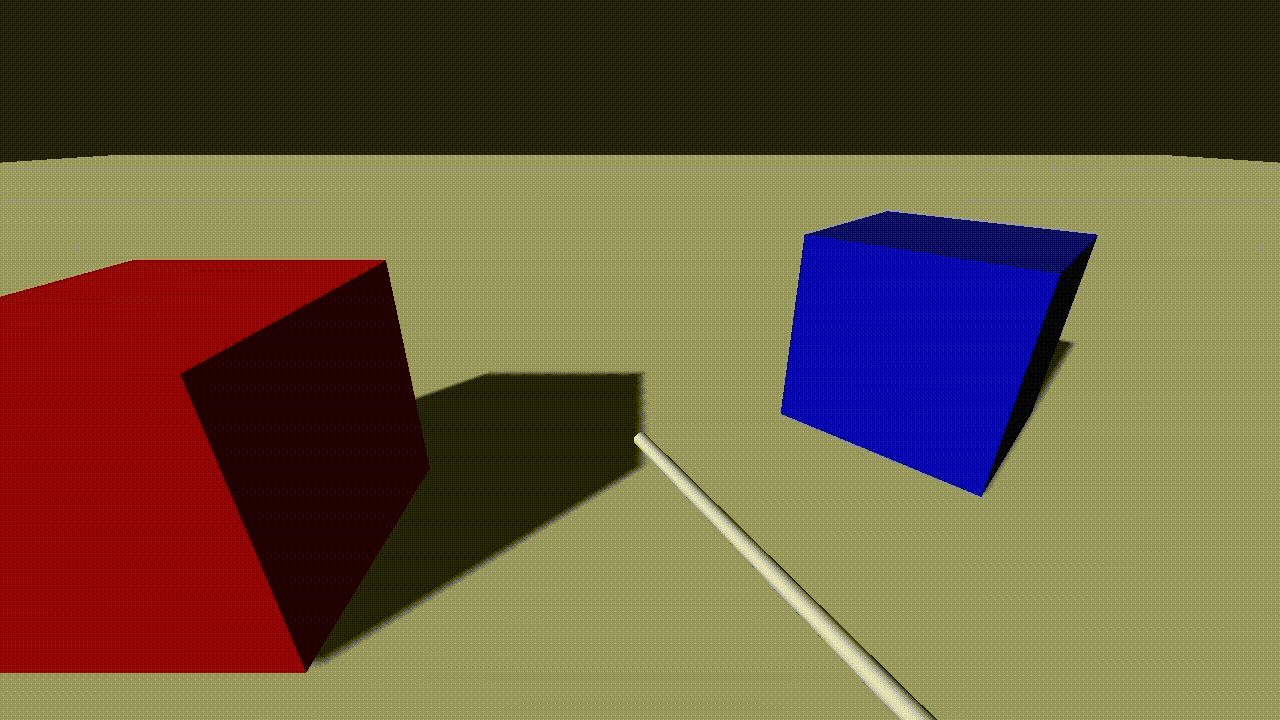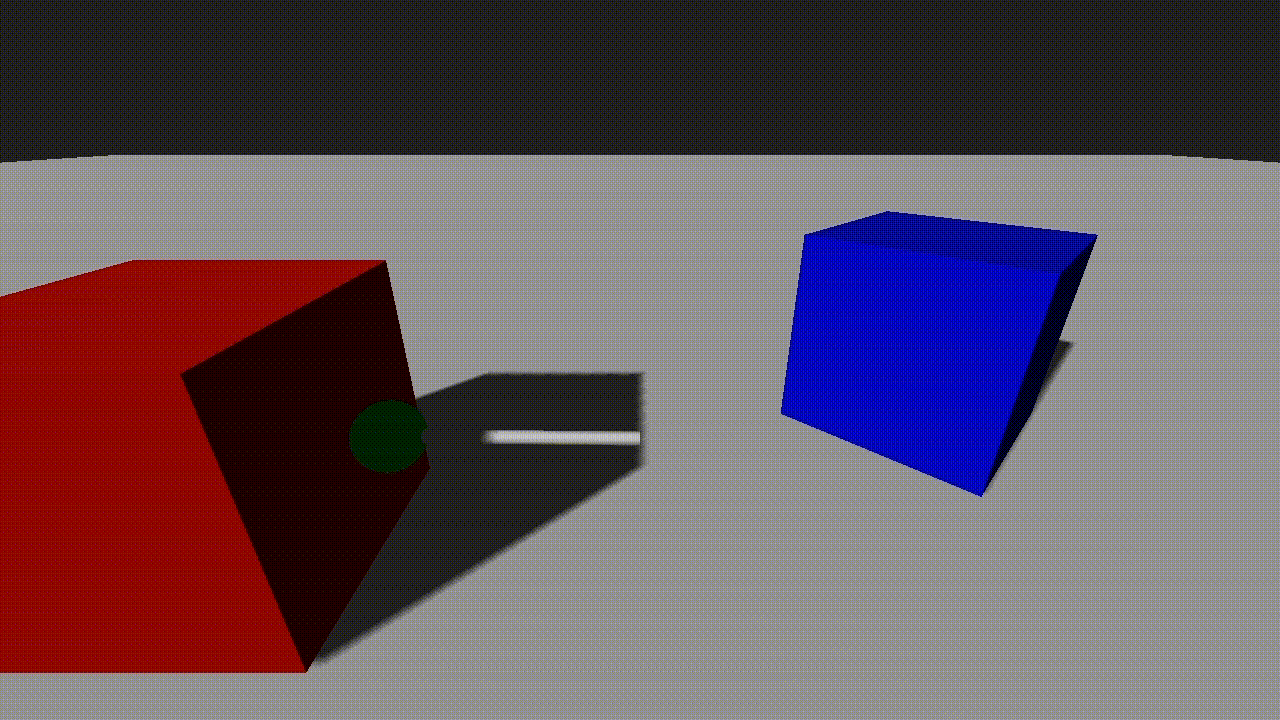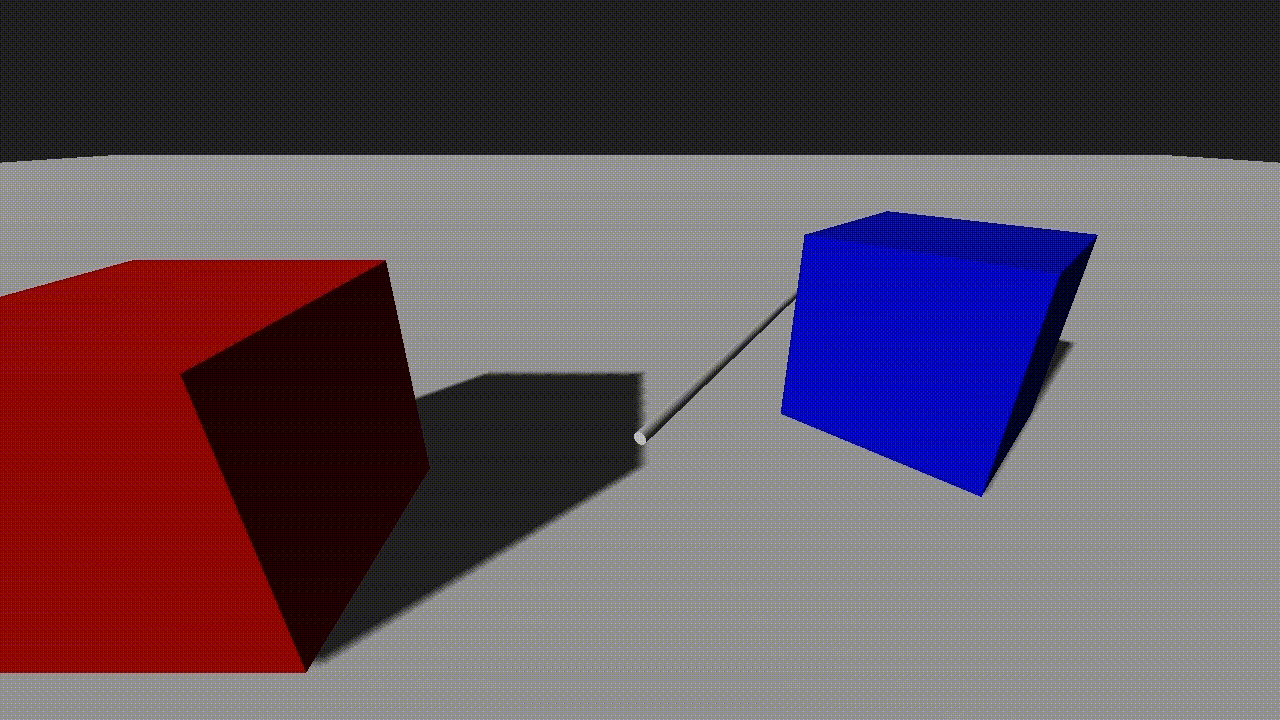
Closest Intersection
The World and Camera Pick methods can perform a line-of-sight test, which will return from the function as soon as the first object is intersected, or they can perform a more thorough test that finds the closest picked object. Both these methods accept an optional closest parameter that uses a boolean to indicate whether the more thorough (and slower) test should be performed.
When we are interested in the intersected object, the closest parameter should be set to true. For example, if we are selecting an object to interact with or shooting a bullet, the closest parameter should be set to true.
If we are not interested in the intersected object, and only want to know if there is an unbroken line of sight between two objects, then the closest parameter can be set to false.
This example shows that if we set the closest parameter to false, the function returns after the first intersection occurs, and does not attempt to find the closest object.
-- Get the displays
local displays = GetDisplays()
-- Create window
local window = CreateWindow("Leadwerks", 0, 0, 1280 * displays[1].scale, 720 * displays[1].scale, displays[1], WINDOW_CENTER | WINDOW_TITLEBAR)
-- Create world
local world = CreateWorld()
-- Create framebuffer
local framebuffer = CreateFramebuffer(window)
-- Set up camera
local camera = CreateCamera(world)
camera:SetClearColor(0.125)
camera:SetPosition(0, 0, -6)
--Create two boxes
local box1 = CreateBox(world, 1, 3, 1)
box1:SetPosition(-1.5,0,0)
local box2 = CreateBox(world, 1, 3, 1)
box2:SetPosition(1.5,0,0)
local model = CreateSphere(world, 0.5)
model:SetColor(1,0,0)
model:SetPosition(8,0,0)
model:SetPickMode(PICK_NONE)
while not window:Closed() and not window:KeyDown(KEY_ESCAPE) do
if window:KeyHit(KEY_SPACE) then
local pickinfo = world:Pick(Vec3(8,0,0), Vec3(-8,0,0), 0.5, false)
model:SetPosition(pickinfo.position)
end
-- Update the world
world:Update()
-- Render the world
world:Render(framebuffer)
endIf we change the closest parameter to true then the closest hit object will be the one returned.
local pickinfo = world:Pick(Vec3(8,0,0), Vec3(-8,0,0), 0.5, true)Entity Pick Mode
Entities can be individually set to be pickable or not, using the Entity:SetPickMode command. Three possible modes are available:
- PICK_NONE: The object will be skipped by all raycasts.
- PICK_COLLIDER: The object's collider will be used for raycasts, if one has been set, otherwise it will be skipped.
- PICK_MESH: The object's mesh geometry will be used for raycasts.
The default pick mode for Model, Brush, and Terrain entities is PICK_MESH. Model primitives like those created with the CreateBox, CreateCone, CreateSphere, and other functions will use the PICK_COLLIDER mode, for greater efficiency.
You can see the effect of the pick mode by disabling picking on one of the boxes in our example above:
b1:SetPickMode(PICK_NONE)Raycast Filter
If a filter callback is provided it will be called for each entity that is evaluated. If the callback returns true the entity will be tested, otherwise it will be skipped.
You can declare this function in the code before the main loop:
function RayFilter(entity, extra)
if entity.color == Vec4(0,0,1,1) then
return false
else
return true
end
endIf we pass the RayFilter function to the Pick command, it will be used to skip blue objects:
local pickinfo = world:Pick(pivot:GetPosition(true), target_pos, 0.0, true, RayFilter)Bouncing Laser Example
Using our newfound knowledge of raycasting, we can now make a much more robust laser bouncing example:
-- Get the displays
local displays = GetDisplays()
-- Create window
local window = CreateWindow("Leadwerks", 0, 0, 1280 * displays[1].scale, 720 * displays[1].scale, displays[1], WINDOW_CENTER | WINDOW_TITLEBAR)
-- Create world
local world = CreateWorld()
-- Create framebuffer
local framebuffer = CreateFramebuffer(window)
-- Set up camera
local camera = CreateCamera(world)
camera:SetClearColor(0.125)
camera:SetFov(70)
camera:SetPosition(0, 2, -3)
camera:SetRotation(25, 0, 0)
-- Add a light
local light = CreateDirectionalLight(world)
light:SetRotation(35, 45, 0)
-- Set up the scene
local floor = CreatePlane(world, 100, 100)
floor:Move(0, -1, 0)
floor:SetColor(0.5)
local b1 = CreateBox(world, 2.0)
b1:SetPosition(-3.0, 0.0, 0.0)
b1:SetColor(1, 0, 0)
b1:SetRotation(0,90,0)
local b2 = CreateBox(world, 2.0)
b2:SetColor(0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
b2:SetPosition(3.0, 0.0, 2.0)
b2:SetRotation(0.0, 45.0, 0.0)
local pivot = CreatePivot(world)
local rod_scale = 5.0
local rod = CreateCylinder(world, 0.05)
rod:SetCollider(nil)
rod:SetParent(pivot)
rod:SetRotation(90.0, 0.0, 0.0)
rod:SetPosition(0.0, 0.0, rod_scale / 2.0)
rod:SetScale(1.0, rod_scale, 1.0)
local sphere = CreateSphere(world, 0.25)
sphere:SetCollider(nil)
sphere:SetParent(pivot)
sphere:SetColor(0, 1, 0)
sphere:SetPosition(0.0, 0.0, rod_scale)
local bounce = CreateCylinder(world, 0.05)
bounce:SetScale(1.0, rod_scale, 1.0)
bounce:SetPickMode(PICK_NONE)
while not window:Closed() and not window:KeyDown(KEY_ESCAPE) do
--Rotate the assembly
pivot:Turn(0.0, 0.5, 0.0)
--Get the point at the maximum ray distance
local target_pos = TransformPoint(0, 0, rod_scale, pivot, nil)
-- Perform a ray cast
local pickinfo = world:Pick(pivot:GetPosition(true), target_pos, 0, true)
--Update the sphere based on the pick result
if pickinfo.entity then
sphere:SetPosition(pickinfo.position, true)
--Show the laser bounce
bounce:SetHidden(false)
--Get the reflection vector
dir = target_pos - pivot.position
dir = dir:Normalize()
r = dir:Reflect(pickinfo.normal)
--Position the laser bounce
bounce:SetPosition(pickinfo.position + r * rod_scale * 0.5)
--Align the Y axis of the laser bounce model to the reflection vector
bounce:AlignToVector(r, 1)
else
sphere:SetPosition(target_pos, true)
bounce:SetHidden(true)
end
-- Update the world
world:Update()
-- Render the world
world:Render(framebuffer)
endThis performs a raycast like before, but the ray will bounce off the surface to form a second ray.

Third-person Player Example
One common use of the raycast feature is controlling the camera's distance from the player in a game that uses third-person view. We can cast a ray in the direction of the camera and use it to detect how far away the camera can be moved without blocking our view of the player.
-- Get the displays
local displays = GetDisplays()
-- Create window
local window = CreateWindow("Leadwerks", 0, 0, 1280 * displays[1].scale, 720 * displays[1].scale, displays[1], WINDOW_CENTER | WINDOW_TITLEBAR)
-- Create framebuffer
local framebuffer = CreateFramebuffer(window)
-- Create world
local world = CreateWorld()
world:SetAmbientLight(0.1)
local light = CreateDirectionalLight(world)
light:SetRotation(45,25,0)
light:SetShadowCascadeDistance(10,20,40,80)
-- Create the ground
local ground = CreateBox(world, 50, 1, 50)
ground:SetPosition(0,-0.5,0)
ground:SetColor(0.5)
-- Create a simple arch
local col1 = CreateBox(world, 1, 3, 1)
col1:SetPosition(3,1.5,0)
col1:SetColor(0,1,0)
local col2 = CreateBox(world, 1, 3, 1)
col2:SetPosition(-3,1.5,0)
col2:SetColor(0,1,0)
local box = CreateBox(world, 7, 1, 1)
box:SetPosition(0,3.5,0)
box:SetColor(0,1,0)
-- Create a camera
local camera = CreateCamera(world)
camera:SetClearColor(0.125)
--Create the player
local player = CreatePivot(world)
player:SetMass(10)
player:SetPhysicsMode(PHYSICS_PLAYER)
player:SetCollisionType(COLLISION_PLAYER)
player:SetPosition(0,0,-2)
player:SetShadows(true)
--Create a visible model for the player
local model = CreateCylinder(world, 0.5, 2)
model:SetPosition(0,1,-2)
model:SetParent(player)
model:SetCollider(nil)
model:SetCollisionType(COLLISION_NONE)
model:SetColor(0,0,1)
--Some variables we will use
local maxcameradistance = 5
local cameradistance = maxcameradistance
local cx = Round(framebuffer.size.x / 2)
local cy = Round(framebuffer.size.y / 2)
local camerarotation = Vec3(35,0,0)
local mousespeed = 0.1
local movespeed = 5
--Prepare window stuff
window:SetCursor(CURSOR_NONE)
window:SetMousePosition(cx, cy)
while not window:Closed() and not window:KeyDown(KEY_ESCAPE) do
--Get the mouse move distance
local mousepos = window:GetMousePosition()
local dx = mousepos.x - cx
local dy = mousepos.y - cy
window:SetMousePosition(cx, cy)
--Calculate the new camera rotation
camerarotation.x = camerarotation.x + dy * mousespeed
camerarotation.y = camerarotation.y + dx * mousespeed
camerarotation.x = Clamp(camerarotation.x, 0, 90)
--Handle player movement
local angle = 0
local move = 0
local strafe = 0
if window:KeyDown(KEY_W) then move = move + movespeed end
if window:KeyDown(KEY_S) then move = move - movespeed end
if window:KeyDown(KEY_D) then strafe = strafe + movespeed end
if window:KeyDown(KEY_A) then strafe = strafe - movespeed end
player:SetInput(camerarotation.y, move, strafe)
-- Update the world
world:Update()
-- Update the camera orientation
camera:SetRotation(camerarotation)
camera:SetPosition(player.position + Vec3(0,1.8,0))
--Perform a raycast from the player's head, in the direction of the camera vector, to the maximum camera range
local pickinfo = world:Pick(camera.position, TransformPoint(0,0,-maxcameradistance, camera, nil), 0.25, true)
if pickinfo.entity then
--If anything was hit, use the pick position as the camera position
cameradistance = pickinfo.position:DistanceToPoint(camera.position)
else
--If nothing was hit then adjust the camera distance to move smoothly to the max distance
cameradistance = Mix(cameradistance, maxcameradistance, 0.1)
end
--Move the camera away from the player
camera:Move(0,0,-cameradistance)
-- Render the world
world:Render(framebuffer)
endWhen the code is run, a raycast is used to ensure a clear line of sight is maintained between the camera and the player.
